VENOUS REFLUX DISEASE
In the human body’s vascular system, arteries carry blood away from the heart and around the body, while veins carry it back. Valves inside the veins help keep the blood from moving backwards. Venous reflux disease (VRD), occurs when veins fail to return blood to the heart properly. The condition most commonly affects the legs. It causes uncomfortable symptoms, such as pain and ulcers, and can worsen without treatment.
DOWNLOAD VENOUS REFLUX DISEASE BROCHURE
Contact AVC to see if our treatment is right for you.
Venous Reflux Disease
Venous Reflux Disease, refers to when the blood in the body backs up abnormally. Blood can pool in the legs and veins because it is not flowing back to the heart. This condition is also referred to as chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) or more widely categorized as vein disease. 40% of people in the United States have venous insufficiency. Women are more likely to have venous reflux, but men still experience it at a significant rate. Most cases occur in those over age 50, but symptoms should not be ignored if they occur earlier.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can also be risk factors in the development of venous reflux. Around 30% of those diagnosed with DVT will experience venous reflux within 10 years.
The Outpatient Difference
When you get treatment at one of AVC’s outpatient labs, you will receive the highest level of exceptional care.
- cutting edge non-surgical procedure
- solves urination problems
- reduced pain & fast recovery
- safe with low rate of side effects
- erectile & sexual functions are maintained
- effective lasting results
- same-day outpatient care
- comfortable sedation/anesthesia
Venous Reflux Symptoms
- Leg Pain
- Leg Swelling
- Cramps
- Heavy or tired legs and feet
- Fatigue
- Throbbing in legs and
- ankles
- Itching in lower extremities
- Burning in lower extremities
- Restlessness/Restless Leg
- Syndrome
- Skin Discoloration/Skin
- Changes
- Ulcers/Open Sores or
- Wounds
How Is Venous Reflux Diagnosed?
Venous reflux is diagnosed with medical history and a physical examination of the legs. An ultrasound is often used to take a closer look at the vessel structure, and to measure blood circulation. Your podiatrist is often a good place to start if you think you may have venous reflux.
If you experience any of the following, contact us to discuss treatment options.
What Are The Treatments for Venous Reflux?
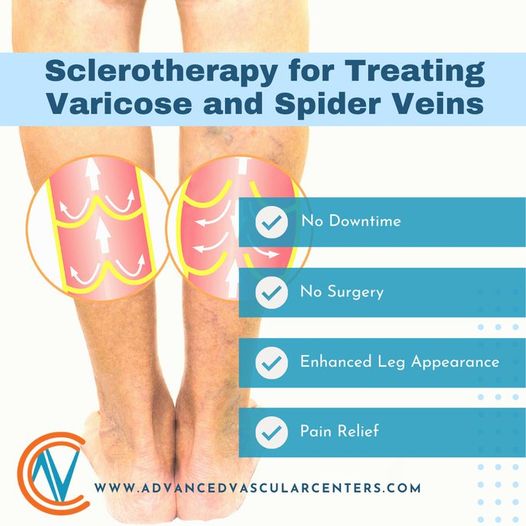
Fortunately, there are a variety of treatments and minimally invasive procedures that can help treat venous reflux. The most common treatment for venous insufficiency is prescription compression stockings. These special elastic stockings apply pressure at the ankle and lower leg. They help improve blood flow and can reduce leg swelling. Sclerotherapy is another procedure used to treat venous reflux. A medicine is injected into the vessels, which makes them shrink. Another procedure we offer is Vein Ablation. Vein Ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that makes use of catheters, lasers, and ultrasound to treat varicose veins.
As doctors, we owe it to YOU, to give you two things:
- All of your treatment options, both surgical and non-surgical.
- Our professional opinion about each of these options for YOU.
FIBROID TREATMENT OPTIONS
Sclerotherapy
- This treatment injects varicose veins with a solution to help them collapse and provide relief of symptoms.
Vein Ablation
- An Interventional Radiologist can use a catheter to administer heat to affected veins. This shrinks the vein, eliminating much of the blood pooling and discomfort.
Compression Stockings
- The first line of defense and treatment of venous reflux are well fitting support hose, also called compression stockings. Your doctor can recommend the best level of compression for you.

APPOINTMENT REQUEST



FAQS
Does venous reflux go away?
Since venous reflux does not heal on its own, medical intervention is often necessary to cure the problem. While there are things you can do to help slow the progression of varicose veins, such as exercise and wearing compression stockings, it will not fix the root cause of the problem.
Is walking good for venous insufficiency?
Exercise is a surprisingly effective treatment for venous insufficiency. Exercising gets your heart pumping, and the extra pumping force of your heart pushes the blood up and out of your lower legs. Walking is particularly beneficial.
Can venous insufficiency affect the heart?
Venous insufficiency doesn’t affect the heart or cause heart problems to progress. On the other hand, existing heart problems, especially congestive heart failure, can make vein problems in the legs much worse depending on the degree of the heart issue.
What is considered severe venous reflux?
A reflux time of >0.5 seconds for superficial veins and 1.0 second for deep veins is typically used to diagnose the presence of reflux. A longer duration of reflux implies more severe disease but does not correlate well with clinical manifestations.
What happens if venous insufficiency is not treated?
Untreated venous insufficiency results not only in a gradual loss of cosmesis but also in variety of complications, the major ones being persistent pain and discomfort, hemorrhage, superficial thrombophlebitis, and progressive skin changes that may ultimately lead to ulceration.
How do you sleep with venous insufficiency?
Something as simple as changing your sleeping position could help reduce varicose veins symptoms. Instead of reclining on your back or stomach, switch to sleeping on your left side. That’s helpful because the body’s largest vein, the vena cava, is on the right side.

